Installation Overview
Overall Architecture
SEB Server is an enterprise server application written in Java and uses Spring and Spring Boot as a main-framework.
The image below shows the overall architecture of the SEB Server which is basically split into two main parts, a webservice and a Graphical User Interface (GUI) service. This two services can be deployed together in one server instance or they can be deployed separately with the ability to scale the webservice for example up to the specified needs.
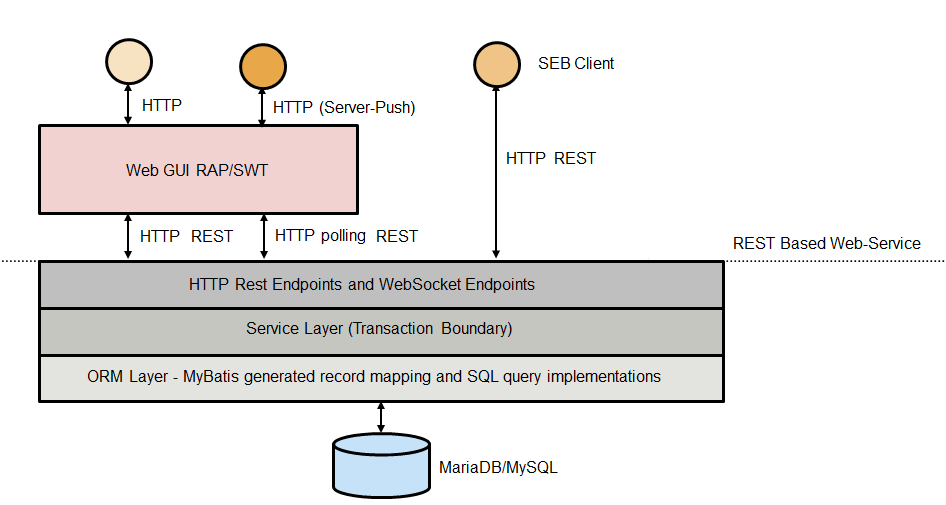
The webservice uses a well defined REST API interface over HTTP and mainly JSON as a data structure for communication. The webservice also implements OAuth2 as a standard authorization and authentication method. The GUI service is written in Java and uses Eclipse RAP to create the HTML front-end and connect to and uses the REST API of the webservice. While the webservice has no user-session based state and externalize state as much as possible (except some internal caching) to make horizontal scaling possible, the GUI service has a session-state for the logged in users as it comes with the RAP framework.
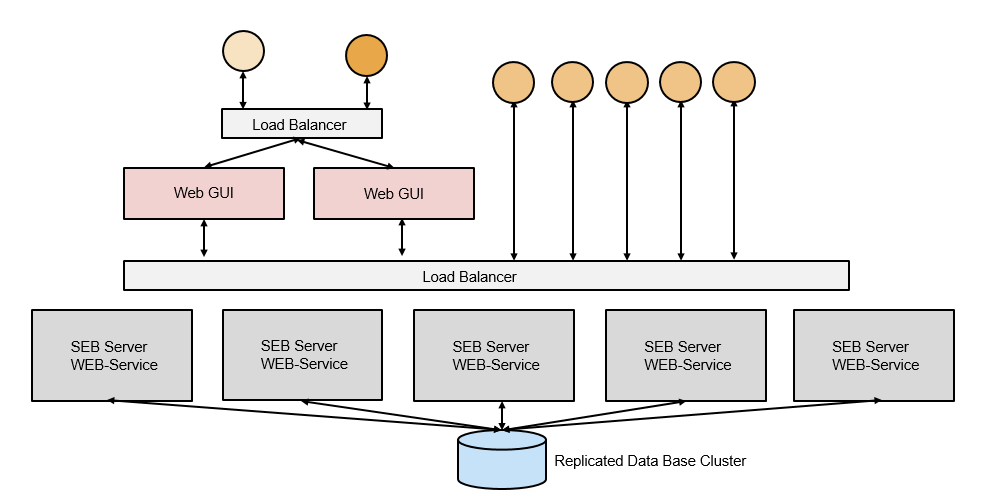
The following diagram shows a setup with scaled web-services covered by a load balancer and a separated GUI service on top. The web-services as well as the GUI service can run on the same host (but separated processes) or they can run in a cluster on different hosts / VM’s.
Note
A Fully clustered setup installation for SEB Server is not yet part of this documentation but it should be possible to achieve this with a docker based cluster service like docker-swarm or Kubernetes and with the given configuration and setup parts.
Installation Repository
The installation and setup of SEB Server depends on the service needs and the local IT environment and infrastructure that exists and can be used. Because the setup can vary from a simple in-house all-in-one server setup to a setup that serves many institutions and must be horizontally scalable, the seb-server-setup repository contains pre-configured docker-based SEB Server setups for the most common cases and can easily be extended by adding new installation setups.
The seb-server-setup repository structure contains different setups-configurations separated for the different needs. Currently only docker-based installations are supported. On the second directory level installation purpose categories like “demo” for setting up a SEB Server for demonstrations, “testing” or “prod” for testing purposes or final productivity setup are defined. The third and forth directory level, if existing, names then different SEB Server setups like “bundled”, “basic”, “tls” or “distributed”. Below is an example of the seb-server-setup directory structure.
- docker
- demo
[a basic bundled test setup]
- prod
- bundled
- basic
[basic bundled setup]
- tls
[bundled setup with tls endpoint]
- cloud
[cloud setup example (Kind)]
- separated
[separated setup without tls]
At each endpoint (e.g.: docker/prod/bundled/basic/) there is a root installation directory with docker-files for the services, a docker-compose definition and a “config” directory containing service related configurations like Spring configuration for the SEB Server, MariaDB configuration for the database and/or reverse proxy configuration.